
#Consider a steam power plant that operates generator#
The electricity generated by the generator is then transmitted through power lines to homes, businesses, and industries, where it serves as a source of electrical power. This can involve cooling water from nearby water bodies, cooling towers, or other heat exchange methods. Cooling System: Steam power plants require a cooling system to dissipate excess heat from the condenser.This process allows for the efficient reuse of the water in the boiler, reducing water consumption and increasing overall efficiency. Here, the steam is cooled and condensed back into water, releasing its latent heat. Condenser: After passing through the turbine, the steam is directed to the condenser.This movement induces an electric current in the wire coils, ultimately producing electrical energy. As the turbine spins, it turns the rotor of the generator, creating a moving magnetic field. Generator: The turbine is connected to a generator, which consists of coils of wire within a magnetic field.
As the steam flows through the turbine, its high-pressure energy is converted into rotational mechanical energy. The turbine is designed with blades that are turned by the force of the steam’s high-speed flow. Turbine: The high-pressure steam from the boilers is directed into a turbine.The generated steam is at high pressure and temperature. This is typically achieved by burning fossil fuels (such as coal, oil, or natural gas) or by using nuclear energy. Boiler: The boiler is responsible for heating water to generate steam.
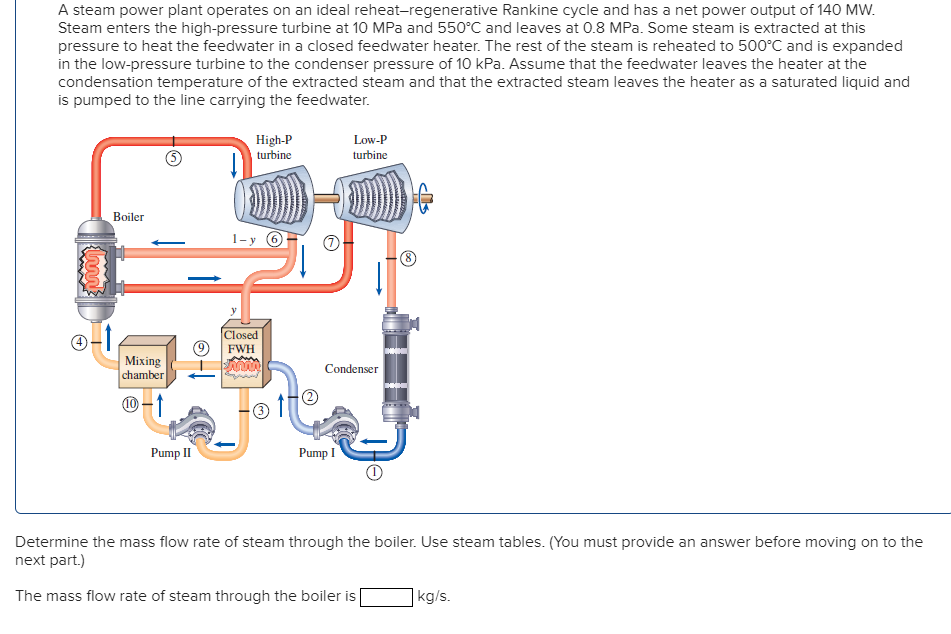
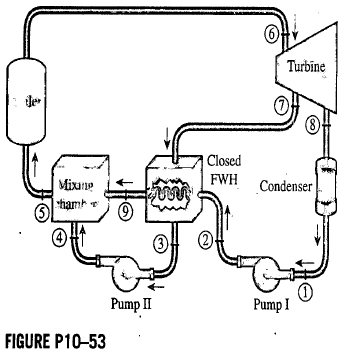
Here’s a breakdown of the key components and their functions within a steam power plant: The primary components of a steam power plant include a boiler, a turbine, a condenser, and a generator. It operates based on the principles of thermodynamics, utilizing the conversion of heat energy into mechanical work and subsequently into electrical energy.
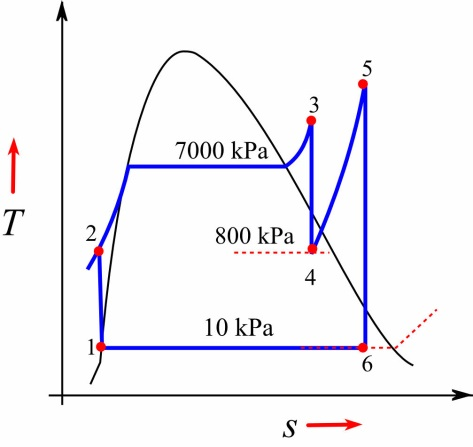
The working system of the Steam Power Plant.Factors to Determine the Site of Steam Power Plant.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
